Congratulations to Yue Mao for his paper accepted by Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy!
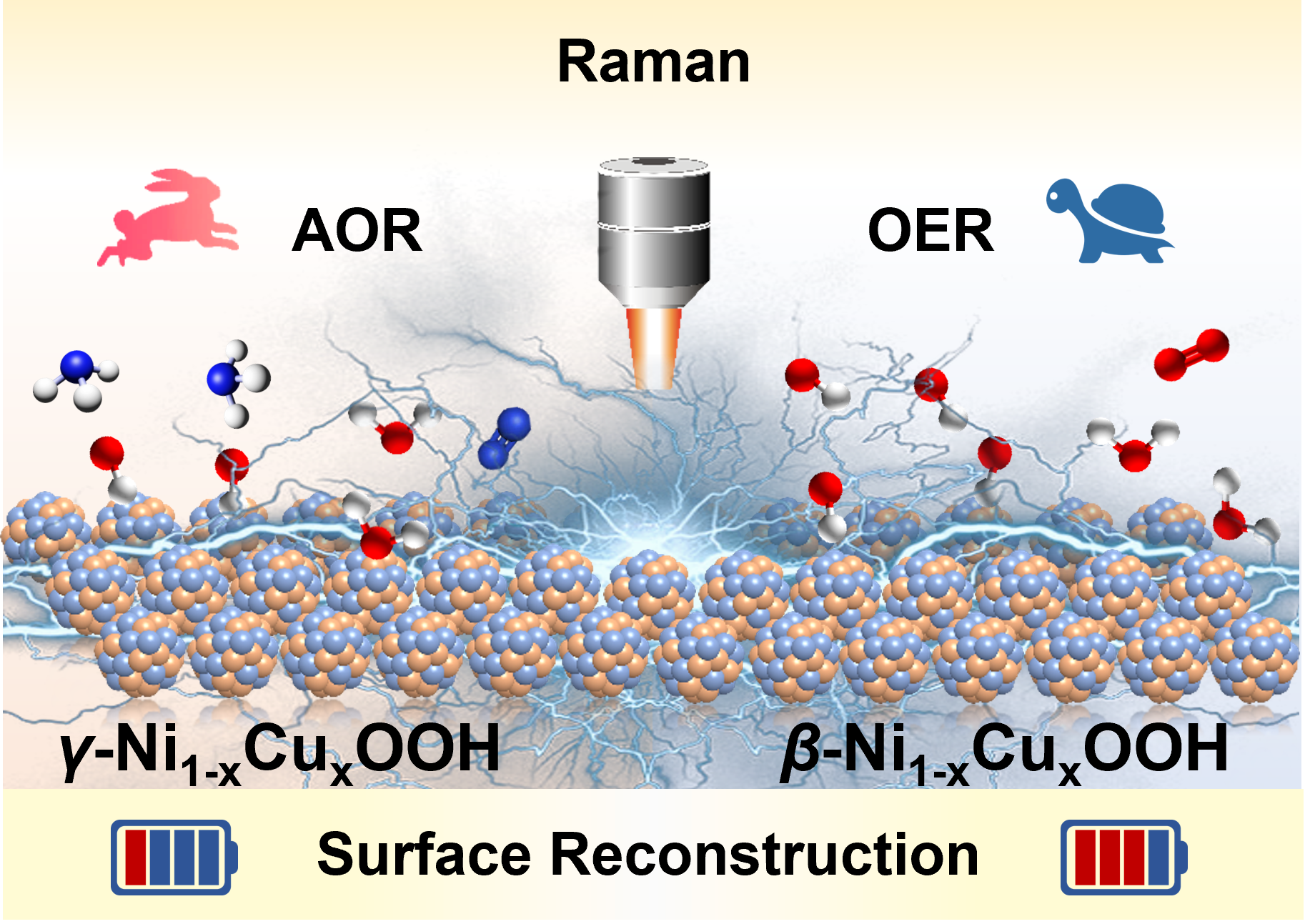
Developing high-performance catalysts and unraveling the structural evolution of the active species are crucial for the large-scale application of ammonia oxidation reaction (AOR). The low-cost Ni-Cu bimetallic catalysts exhibit a bright prospect due to its high catalytic activity and stability. Here, in situ Raman spectroscopic study of the surface reconstruction behaviors of Ni-Cu alloy nanoparticles (NPs) indicates that γ-Ni1-xCuxOOH formed at lower potentials acts as the ultimate catalytic center in alkaline AOR. Density functional theory calculations confirm that γ-Ni1-xCuxOOH optimizes the *NH3 adsorption and *N2 desorption capacity and reduces the energy barrier in rate-determining step (*NH3→*NH2). As a proof-of-concept, the Ni0.8Cu0.2 NPs show a maximum current density of 229.63 mA cm−2 at 1.69 V vs. RHE, along with sustained stability over 100 h @10 mA cm−2. This study identifies the real active species of Ni-Cu alloy catalysts in AOR, and provides insights for the design of more efficient and advanced catalysts.